SoftBank’s IoT Strategy to Bypass the Internet
SoftBank has announced that it has succeeded in completing the world’s first connection test in a commercial environment for NIDD (Non-IP Data Delivery), which has been newly defined in the 3GPP for NB-IoT, the LTE communication standard for IoT devices. Accordingly, SoftBank will solicit service providers and launch experimental services in a commercial environment.
NIDD is a new technology that enables users to transmit data to IoT devices without allocating an IP address. By not using an Internet protocol in transmission, the risk of being subjected to a malicious attack targeting an IoT device is low, making it possible to build a highly secure network. Through the elimination of the data such as header information additionally required in conventional data communications, the electric power needed for communication is reduced and, in addition to extending battery life, a broader area can be covered. Furthermore, by enabling connection on a closed network with IoT platforms provided by service providers and with external application servers, it is possible to build a highly secure network from end to end.
Image of Data Communication Using NIDD Technology
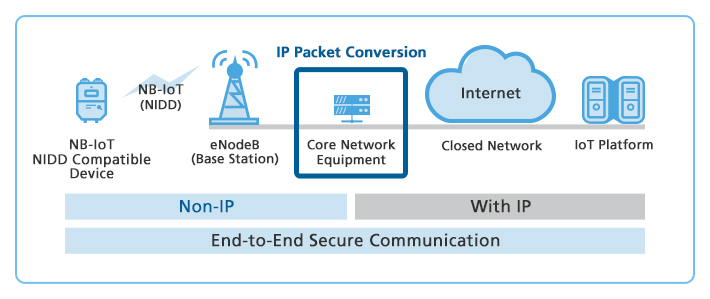
With the introduction of NIDD technology, in addition to the conventional NB-IoT and Category M1 (Cat. M1) services it currently provides, for which an IP address is allocated, SoftBank aims to introduce and commercialize devices tailored to various businesses and fields such as crime prevention, social infrastructure and agriculture, making full use of its distinctive features of high security, low power consumption, and high area coverage.
Get Coverager to your inbox
A really good email covering top news.Betterfly raises $60 million






